introductory
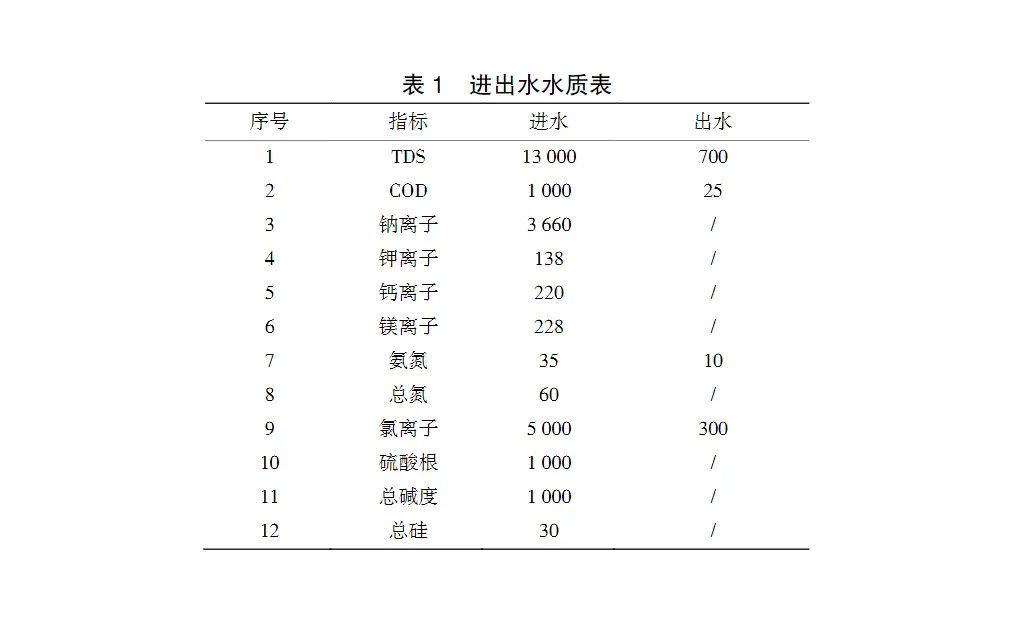
Biopharmaceutical enterprises use soybean oil, corn starch, betaine, corn germ, corn protein powder, soybean meal, cottonseed protein and other raw materials to produce vitamin B12, methylcobalamin, vitamin B2, adenosylcobalamin and other APIs. The production process generates about 3000 m3-d-1 of wastewater with high salt and high organic matter, which is discharged after biochemical treatment to meet the standard. In order to save water resources, the enterprise new wastewater zero-discharge process, the effluent water quality to meet the "recycled cooling water reclaimed water quality standards" (HG/T3923-2007) standards [1], the reuse rate of not less than 95%. Concentrate for evaporation and salt separation, evaporation and crystallisation of by-products of sodium chloride to meet the GB / T 5462 -2015 "Industrial Salt" industrial dry salt secondary standards, the rate of impurity salt is less than or equal to 15% [2-5].1 Zero-discharge process 1.1 Water quality The wastewater is high in salt, chloride ions, sodium ions and other monovalent ions account for the total salt ratio is high, and the design of the incoming and outgoing water quality is shown in Table 1, and the units are mg-L-1.
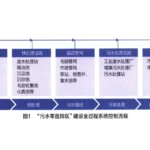
1.2 Process flow as shown in Figure 1, water reuse and zero discharge process for "pretreatment system + NF system + NF concentrate reduction system + RO system + secondary dehardening to remove silica system + high-pressure HPRO concentration + subsequent MVR evaporation and cryocrystallisation system". The processing idea of the whole system is to separate COD, divalent salt and monovalent salt through nanofiltration membrane retention, and then separate COD and divalent salt and monovalent ions in NF concentrate through material membrane, so that the divalent salt and COD in the whole sewage are enriched in the secondary concentrate of the reduced concentrate and the primary concentrate, and the COD in the concentrate after the primary reduction is non-biochemical degradation of COD, which can be improved by advanced oxidation technology to improve biochemical degradation. The COD in the concentrated liquid after the first reduction is non-biochemical degradable COD, which is used as the carbon source of the biochemical system after improving the biochemistry through advanced oxidation technology. The concentrate after secondary reduction mainly contains most of the divalent salts, which can be removed by the subsequent freeze crystallisation unit. The clear liquid after treatment by NF and NF reduction units contains mainly monovalent salts, at which point the salt concentration can be carried out. After RO treatment, the total hardness of calcium and magnesium in the concentrated liquid rises, and the hardness, alkalinity and total silica are removed through the synergistic removal of the per-caustic soda-soda ash-magnesium chloride agent [6]. For the subsequent HPRO re-concentration as a front-end guarantee pretreatment, HPRO concentrate for high TDS, high COD. can through the NF into the NF clear liquid of organic matter molecular weight, most of which belongs to the volatile substances, will not have a greater impact on the subsequent MVR evaporation operation process. Therefore, the main idea for the first separation of COD and divalent salt, a salt concentrate evaporation salt crystallisation, divalent salt concentrate freezing crystallisation, COD by oxidation pretreatment into the biochemical system to deal with, so as to achieve the purpose of zero emission. The whole process consists of pretreatment system, NF system, NF concentrate reduction system, reverse osmosis system, softening system, HPRO system, sludge disposal system, seven major components.
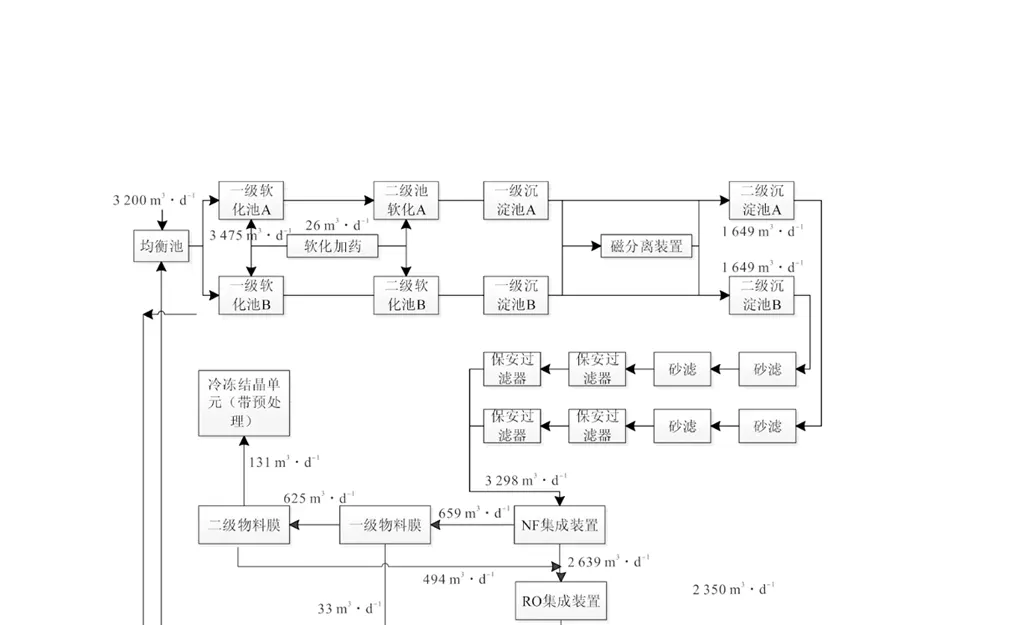
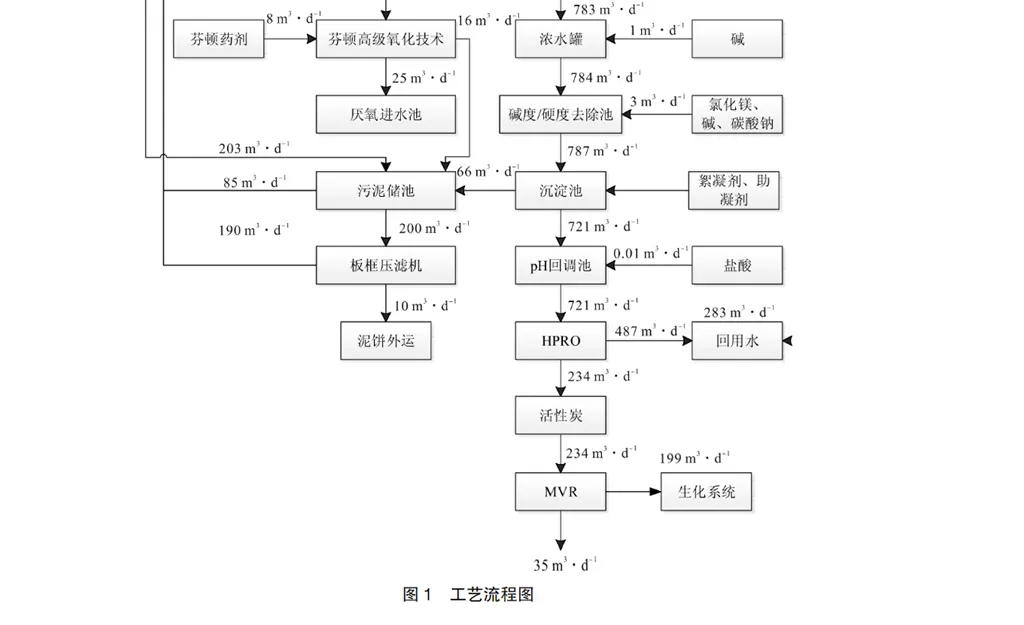
Pre-treatment system includes: hardening and softening system, magnetic separation system, sand filter, security filtration system, etc. NF system includes: NF inlet pump, NF inlet tank, NF integrated equipment, NF clear liquid tank, NF concentrate tank and other ancillary dosing units, etc. RO system includes: RO inlet pump, RO integrated equipment, RO concentrate tank, and scale inhibitor required for the RO system, such as dosing and cleaning units, etc. NF concentrate reduction system includes: a feed pump, two feed pumps, a booster pump, two booster pumps, intermediate tanks, storage tanks at all levels of materials and other units, cleaning and dosing units. Deep softening system: including pH adjustment tank, calcium and magnesium precipitation area and hardness removal reaction area. Sludge disposal system includes: diaphragm-type plate and frame filter press, press pump, press tank, belt conveyor, dewatering clear liquid conveyor pump, sludge hopper, flap system, sludge storage tank, plate and frame feed pump, and so on.
2 Parameters of major structures and equipment
2.1 Pre-treatment system Biochemical system of the second sedimentation tank effluent presents high COD, high suspended solids, high hardness characteristics, in order to meet the minimum requirements of the NF influent, it is necessary to carry out pre-treatment to precipitate COD, calcium and magnesium hardness and TSS, etc. first. Then sand filter and security filter to retain the suspended solids and organic matter that are not completely precipitated. The main role of raw water pretreatment is to prevent fine particles from contaminating the NF membrane; to prevent colloidal substances from contaminating and clogging the NF membrane; and to prevent oxidative damage to the NF membrane by strong oxidants. The project design adopts the combination of "softening in addition to hardness + magnetic separation + sedimentation + sand filtration + security filters" to pre-treat the original biochemical system of the two sedimentation tank water. There are 4 softening reaction areas, each with a capacity of 50 m3, dosing sodium hydroxide, magnesium chloride, calcium oxide, sodium carbonate, 2 sedimentation tanks, each with a capacity of 275 m3, sedimentation time of 3 h. There are 4 sets of sand filtration equipment, with a single set of processing capacity of 70 m3-h-1 and a filtration speed of 10 m-h-1. There are 2 sets of security filters, with folded high-flow cartridges, with a length of 1,016 mm, and a filtration precision of 5 μm.
2.2NF system biochemical system after treatment of the secondary sedimentation tank effluent difficult to biochemical degradation of organic matter formed COD, salinity and chromaticity exceeded the serious, after the front-end pretreatment system, the effluent suspended solids, hardness is greatly reduced, but the COD, salinity and so on is still very high. NF using integrated modular device, according to the design of 3,298 m3-d-1, a total of four sets of 900 m3-d-1NF integrated equipment, total capacity of 3600 m3-d-1. Single set of 9 membrane shells, 54 membrane elements, a total of 216 membrane elements, designed membrane flux 16 LHM, designed production capacity of 16 LHM. 1NF integrated equipment, a total treatment capacity of 3600 m3-d-1, a single set of configuration 9 membrane shells, 54 membrane elements, a total of 216 membrane elements, the design of the membrane flux 16 LHM, the design of the water production rate of 80%.
2.3 RO system using RO system will be monovalent salt concentration, clear liquid reuse, RO membrane concentration of liquid volume into the high-pressure HPRO for further concentration treatment, as far as possible to reduce the amount of evaporation.RO using integrated modular device, according to the design of 3200 m3-d-1, a total of 4 sets of capacity of 800 m3-d-1 RO integrated equipment, a single set of configuration of 12 membrane shells, 72 membrane elements, a total of 288 membrane elements, designed membrane flux of 12 LHM, design yield 75%. Total 288 membrane elements, design membrane flux 12 LHM, design water yield 75%.
2.4 NF concentrate reduction system For the characteristics of NF membrane concentrate with high COD and high divalent salt, in order to improve the overall water resource recovery rate, COD and divalent salt need to be separated. A total of four sets of integrated equipment for NF concentrate reduction are designed for this project. The single set is divided into two stages of separation, with the first stage divided into two sections, one section of clear liquid from the first stage enters the second stage to ensure the COD of the clear liquid effluent, and one section of concentrated liquid from the first stage enters the first stage of the second stage for re-concentration, which reduces the amount of the tailing of the NF concentrate to the maximum extent. The clear liquid produced by the reduction system is mixed with the nanofiltration clear liquid to carry out reverse osmosis treatment, the first two sections of the concentrated liquid by the original Fenton advanced oxidation technology to improve the biochemical system, then enter the original anaerobic unit for treatment, the second stage of the concentrated liquid enters the freezing crystallisation unit to carry out the sodium sulphate crystallisation. n F concentration liquid reduction and concentration module device, according to the design of 659 m3-d-1, 495 m3-d-1 of water, the design of the Primary membrane flux 12 LMH, secondary membrane flux 5.8 LMH, total number of membrane elements 112.
2.5 Depth softening system RO concentrate is enriched with most of the calcium, magnesium and other divalent ions in the NF produced water as well as silica, which has a strong tendency of scaling and fouling in the subsequent HPRO treatment system, and therefore needs to be chemically softened [8]. Depth softening reaction area 4, a single pool capacity of 30 m3, dosing order were sodium hydroxide, magnesium chloride, calcium oxide, sodium carbonate, sedimentation tank 2, a single pool capacity of 150 m3, sedimentation time of 6 hours.
2.6 HPRO system RO concentrate is still 721 m3-d-1, directly on the evaporation and crystallisation, then the investment and operating costs will be high, after the material balance calculation and ion concentration estimation, the TDS of RO concentrate is about 35,000 mg-L-1, through the HPRO to further concentrate the TDS to about 100,000 mg-L-1, the amount of water into the evaporation can be reduced to 234 m3-d- 1 [9]. 1[9].The HPRO is an integrated modular unit designed according to 730 m3-d-1 with 84 membranes, a design membrane flux of 10 LHM, and a design water yield of 60%.
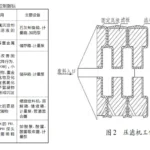
2.7 Sludge disposal system The sludge generated by this project is mainly softening process, Fenton oxidation system, coagulation and precipitation system generated by the chemical sludge is mainly, moisture content of 95% ~ 98% between the cohesive properties, the main components of calcium carbonate, magnesium hydroxide, magnesium silicate, calcium silicates, calcium silicate, ferric hydroxide, and some of the flocculants and organic pollutants [11], suitable for the selection of plate and frame filter presses For treatment, the design adopts 2 sets of high-pressure diaphragm dewatering machine, with a single filtration area of 200 m2, a feeding capacity of 297 m3-d-1, a supporting feeding pump of 40 m3-h-1, a synchronous supporting discharge silo, sludge thickening tank, etc., and the water content of the dewatered sludge is 60%~70%.
3 Running Costs Running costs include chemicals, electricity and labour. Calculated on the basis of the project's water treatment capacity of 3200 m3-d-1, the steam is on-site waste heat steam, which is not costed, and is offset by the proceeds from the finished salt of sodium chloride and sodium sulphate and the disposal fee.
(1) Pharmaceutical costs: including membrane cleaner, scale inhibitor, hydrochloric acid, coagulant aid, flocculant, magnesium chloride, sodium carbonate, sodium hydroxide, calcium oxide, hydrogen peroxide, ferrous sulphate, biocide and reducing agent a total of 12 kinds of chemicals, the cost of treatment of tonnes of water is about 13.23 yuan;
(2) Electricity: the total operating power of the sewage treatment system equipment running every day is 1593.347 kW. the maximum daily electricity consumption for tonnes of water is: 1593.47 kW × 0.8 × 24h ÷ 3200m3 = 9.56 kW-h-m-3. industrial electricity is calculated at 0.407 yuan - (kW-h)-1. The electricity cost for tonnes of water treatment is 3.89 yuan-m-3.
(3) Labour cost: the project requires a total of about 24 personnel, estimated at 100,000 yuan/person-year, the labour cost of tonnes of water is about 2.27 yuan. The comprehensive operating cost is about 19.39 yuan-m-3, of which the cost of pharmaceuticals will change with the change of water quality and quantity.
4 Conclusion
(1) The wastewater generated by biopharmaceuticals can be treated by biochemical system and the standard water can be reused by way of hardness removal, filtration and membrane separation to achieve water reuse, and the water quality reaches the Water Quality Standard for Recycled Water of Circulating Cooling Water (HG/T3923-2007).
(2) The mono- and divalent salts in the wastewater can be separated by the NF nanofiltration membrane integrated equipment, and the NF concentrate can be separated by two-stage material separation membrane to achieve the separation of COD and salts, which further reduces the volume of the NF concentrate and at the same time reduces the COD value of the influent of the sodium sulphate evaporation and crystallisation system, and improves the quality of the sodium sulphate crystalline salt.
(3) The clear liquid after separation by NF membrane system is concentrated by RO and HPRO, which effectively reduces the scale of sodium chloride evaporation and crystallisation system and saves investment and operation cost.
(4) The setting of the softening and hardening system reduces the cleaning frequency of the membrane, which can improve the service life of the membrane.
(5) Overall water reuse rate of 95% or more.
Welcome to call us for consultation, technical exchange, and material experiment.
 Plate and frame chamber diaphragm filter presses
Plate and frame chamber diaphragm filter presses