Filter press as a widely used in solid-liquid separation equipment, its welding process selection for the performance and service life of the equipment has an important impact. In this paper, we will analyse the welding process of filter press in detail, discuss the advantages and disadvantages of different welding methods, and provide corresponding welding recommendations for different materials and structures to help readers better understand and select the appropriate welding process.
I. Analysis of the welding process of the filter press
Filter press welding processes mainly include fusion welding, pressure welding and brazing. Different welding processes have their own advantages and disadvantages and are suitable for different materials and structures.
1. Melt welding
Melt welding is the process of heating two pieces of metal to a molten state and then joining the molten metal together by means of filler material, which is left to cool and form a weld. Melt welding mainly includes arc welding, gas welding and laser welding.
Arc welding is the most common melting welding method, with the advantages of simple equipment, adaptability and low cost. It is suitable for welding most metal materials, especially stainless steel, carbon steel and alloy steel. Gas welding is to use a gas flame to heat the metal to a molten state, suitable for welding of thin plates. Laser welding, on the other hand, has the advantages of high energy density, precise control, fast speed, etc. It is suitable for welding of precision parts.
2. Pressure welding
Pressure welding is the joining of two pieces of metal together by applying pressure without the need for filler material. Common pressure welding methods include resistance welding, friction welding and ultrasonic welding.
Resistance welding involves heating the metal to a plastic state by the resistive heat generated by an electric current at the point of contact between two pieces of metal, and then applying pressure to join the metals together. Resistance welding is suitable for welding thin sheet materials such as stainless steel and aluminium alloys. Friction welding is the process of joining two pieces of metal by rotating or vibrating them to generate frictional heat, which heats the metal to a plastic state and applies pressure. Friction welding is suitable for welding long rods, tubes and shafts. Ultrasonic welding uses ultrasonic vibration energy to join two pieces of metal together, and is suitable for joining materials such as plastics, ceramics and metals.
3. Brazing
Brazing is a method of joining two pieces of metal together using a brazing alloy. The brazing alloy melts at high temperatures, wetting and filling the gaps between the metals, and forms a strong joint when it cools. Brazing is suitable for welding dissimilar materials, such as copper and stainless steel, aluminium and steel.
Second, the choice of filter press welding process recommendations
When selecting a welding process for a filter press, factors such as equipment structure, material properties, usage requirements and production costs need to be considered. The following are some suggestions for selection:
1. Electric Arc Welding (EAW): EAW is a cost-effective alternative for welding most metallic materials such as stainless, carbon and alloy steels. It has wide applicability and low cost.
2. Laser welding: Laser welding is a good choice for precision parts or where high precision welding is required. It enables precise control and high speed welding to improve productivity.
3. Resistance welding: For welding thin sheet materials, such as stainless steel and aluminium alloys, resistance welding is a suitable option. It reduces distortion and residual stress and improves weld quality.
4. Friction welding: Friction welding is an efficient and reliable welding method for welding long rods, tubes and shaft parts. It enables fast and stable welded connections.
5. Brazing: Brazing is a suitable option for welding dissimilar materials or where filler materials are required. It enables reliable connections and is adaptable to different material combinations.
III. Examples of the application of filter press welding process
In order to better understand the selection and application of filter press welding processes, a few examples are listed below:
1. Carbon steel filter presses: Carbon steel filter presses are usually manufactured using electric arc welding. As carbon steel has good electrical and thermal conductivity, the arc can quickly melt the filler material and form a reliable joint. Arc welding is less expensive and suitable for mass production.
2. Stainless steel filter press: Stainless steel has better corrosion resistance and beautiful surface quality, and is usually manufactured by laser welding or argon arc welding. Laser welding can achieve high precision and high speed welding, suitable for small or precision parts manufacturing. Argon arc welding can protect the surface of stainless steel from oxidation and maintain its original beauty and quality.
3. Aluminium filter presses: Aluminium alloys have the advantages of being lightweight and corrosion-resistant, and are usually manufactured by resistance welding or brazing. Resistance welding can reduce the deformation and residual stress of aluminium alloy and improve the welding quality and service life. Brazing, on the other hand, is suitable for the connection of aluminium alloy with other metals, such as copper alloy and other dissimilar materials.
4. Long bar presses: Friction welding is an efficient and reliable method for the fabrication of long bar presses, such as welded connections of tubes and shaft parts. It generates frictional heat by rotation or vibration, heats the metal to a plastic state and applies pressure to achieve the connection. This method is suitable for the manufacture of large or special shaped long bar stock parts.
5. Plastic-to-metal filter presses: for plastic-to-metal connections, e.g., plastic feed pipes to metal bodies
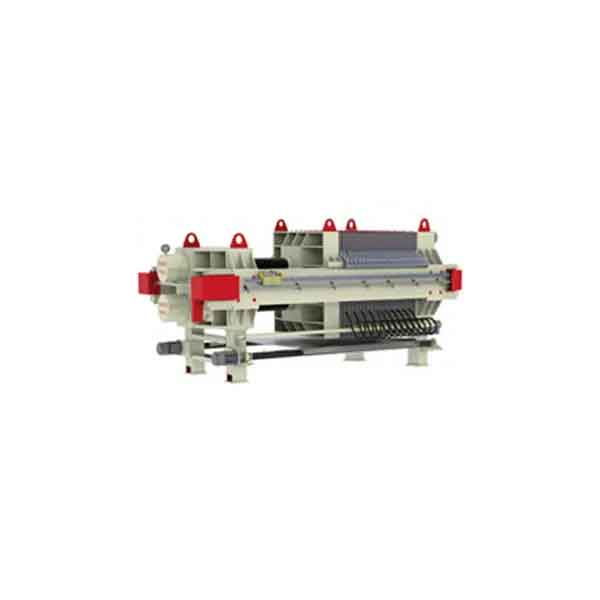
 Plate and frame chamber diaphragm filter presses
Plate and frame chamber diaphragm filter presses